When a child is diagnosed with a tumor, it is, understandably, every parent’s worst nightmare. While pediatric cancers are thankfully rare, recognizing the specific types of tumors that affect the urinary tract and reproductive organs is crucial for seeking the correct and most timely treatment. These tumors require a very specialized approach, which is why understanding the role of a pediatric urologist is essential.
You might be asking, What is the difference between a pediatric urologist and other specialists? Simply put, a pediatric urologist is uniquely trained to manage both the surgical and functional complexities of a child’s developing genitourinary system. This guide is dedicated to outlining the most common pediatric urological tumors, their treatment options, and the vital role played by experts in this highly specialized field.
Understanding Pediatric Urological Tumors
Pediatric urological tumors are masses that arise in the kidneys, adrenal glands, bladder, or reproductive organs of children. Their management demands a multidisciplinary team, including oncologists, radiologists, and, critically, a Pediatric Urologist in India.
A. The Rarity and Specificity of Pediatric Tumors
Childhood tumors differ significantly from those found in adults. They often grow faster and respond differently to treatment. For the urinary tract, the vast majority of pediatric tumors occur in the kidneys.
B. What is the difference between a pediatric urologist and other specialists?
This is a key question in managing these rare and complex conditions:
- Pediatric Urologist: They are surgeons who specialize in the urinary and reproductive systems of children. Their role is often focused on the surgical removal of the tumor (e.g., radical or partial nephrectomy) and managing any resulting complications, such as preserving remaining kidney function or reconstructing the urinary tract. Their training allows them to perform delicate, child-sized procedures.
- Pediatric Oncologist: This physician handles the medical treatment of cancer, including chemotherapy and radiation therapy, which often occur before or after surgery.
- Pediatric Surgeon in Delhi: While a general pediatric surgeon handles a wide range of childhood operations, a भारत में बाल चिकित्सा मूत्र रोग विशेषज्ञ has specialized expertise specifically in the genitourinary organs, which is paramount for achieving complex surgical margins and functional outcomes.
Common Pediatric Urological Tumors and Their Management
Pediatric tumors in this system can be broadly categorized by their location: kidneys and gonads.
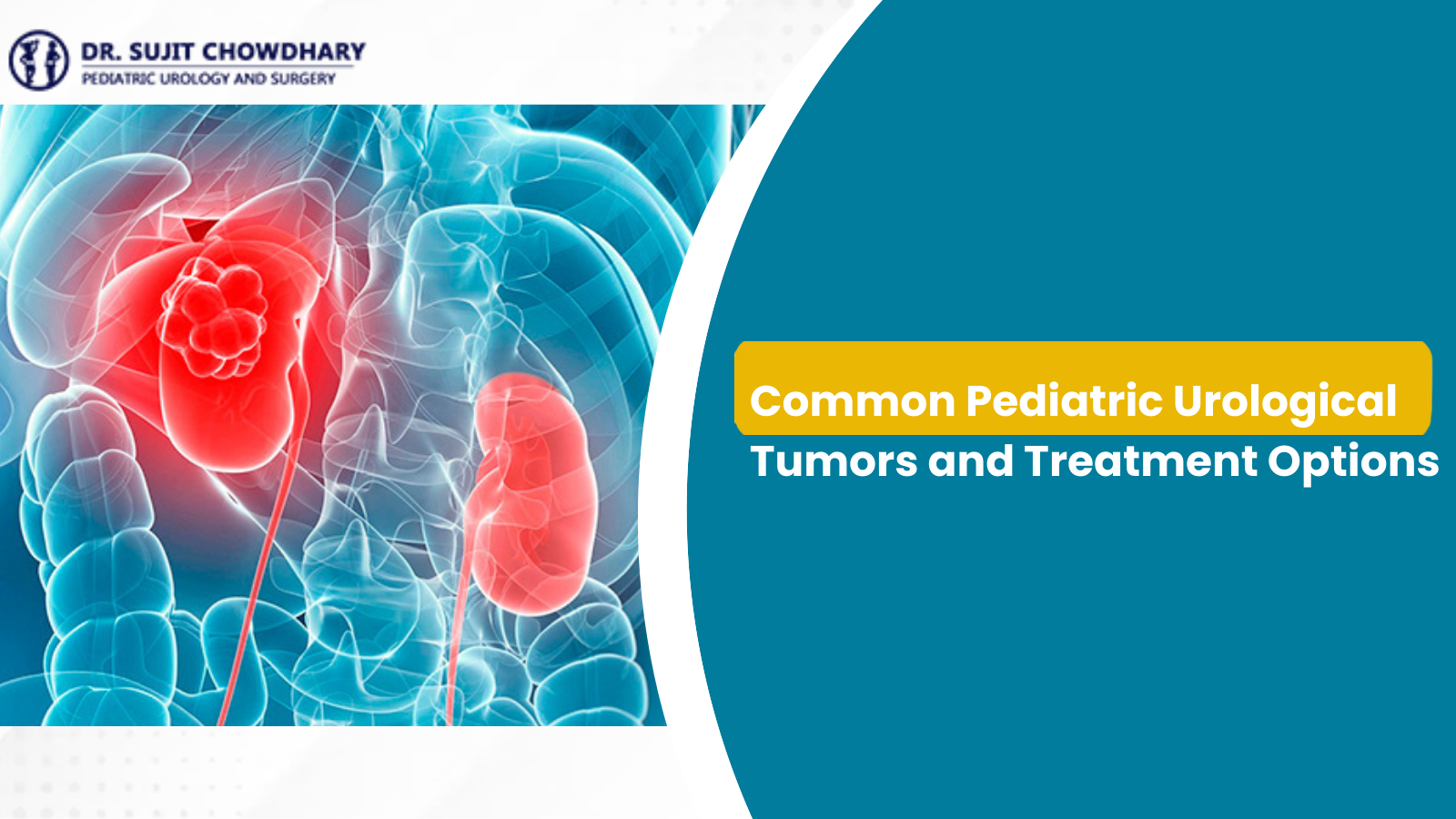
A. Kidney Tumors: Wilms Tumor (Nephroblastoma)
Wilms tumor is the most common kidney cancer in children and the fourth most common pediatric malignancy overall. It typically affects children between the ages of two and five.
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
- Abdominal Swelling/Mass: This is the most common presentation. Parents often notice a firm, painless mass in the child’s abdomen.
- Abdominal Pain
- Fever, Hematuria (blood in the urine), or Hypertension (high blood pressure).
Treatment Options:
Wilms tumor management is highly standardized globally, relying on a multimodal approach directed by staging.
- Chemotherapy (Pre-operative): In most major protocols (especially outside North America), chemotherapy is administered before surgery (neoadjuvant) to shrink the tumor, making the operation safer and potentially allowing for kidney-sparing surgery.
- Surgery (Radical or Partial Nephrectomy): The Pediatric Urologist in India is responsible for the surgical phase.
- Radical Nephrectomy: Removing the entire affected kidney, which is the most common procedure.
- Partial Nephrectomy: For smaller tumors or those involving both kidneys, the urologist works to remove only the tumor while preserving as much healthy kidney tissue as possible, crucial for long-term health.
- Post-operative Chemotherapy/Radiation: Depending on the stage and pathology of the tumor after removal, further chemotherapy or localized radiation may be necessary.
B. Tumors of the Gonads (Testicular and Ovarian)
While some testicular tumors are benign, many are malignant and require careful, prompt management.
Testicular Tumors (Most Common in Boys)
Tumors in the testes often present as a firm, painless lump in the scrotum. The most common types in children are Yolk Sac Tumors and Teratomas.
- Diagnosis: Ultrasound and specific blood tumor markers (AFP and hCG).
- Treatment: Initial treatment involves a radical inguinal orchiectomy (surgical removal of the testicle through an incision in the groin, not the scrotum, to prevent spread). Following surgery, chemotherapy or surveillance is determined by the tumor type and stage.
Ovarian Tumors (In Girls)
Ovarian masses are often diagnosed when they cause acute abdominal pain due to twisting (torsion). While most are benign cysts, malignant tumors like Germ Cell Tumors must be ruled out.
- Treatment: Surgery to remove the mass or the affected ovary. Preserving fertility is a major consideration, often requiring consultation with the Pediatric Urologist in India and oncologist.
The Specialist’s Advantage: Expertise and Technology
The surgical treatment of pediatric urological tumors is fundamentally different from adult tumor surgery. Children have smaller organs, more complex vascular structures, and a lifetime of growth ahead of them. This is where the specialized training of a Pediatric Urologist in India becomes indispensable.
A. Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS)
Modern treatment protocols favor minimally invasive approaches whenever possible, reducing recovery time and minimizing trauma.
- Laparoscopic and Robotic Surgery: For tumors like Wilms tumors or complex kidney masses, highly trained surgeons, such as डॉ. सुजीत चौधरी , use robotic or laparoscopic techniques to perform nephrectomy through tiny keyhole incisions. This demanding work requires specialized skill to manipulate instruments in a confined space while maintaining oncologic principles (no tumor spillage). Dr. Chowdhary’s expertise in this area is a significant benefit for young patients.
- Preserving the Kidney: In children, maximizing the function of the remaining kidney tissue is a long-term health goal. MIS techniques often allow for more meticulous partial nephrectomy, which is a major focus for a Pediatric Urologist in India treating bilateral or single-kidney tumors.
B. The Role of the Multidisciplinary Team
The successful management of pediatric tumors is never done in isolation. The team approach is crucial:
- Pediatric Oncologist: Manages the systemic effects and chemotherapy.
- Pediatric Radiologist: Provides high-resolution imaging and guides biopsies.
- Pathologist: Determines the specific type and aggressiveness of the tumor.
- Pediatric Urologist: Provides surgical expertise for removal and manages the functional urinary consequences of treatment.
Long-Term Follow-up and Prognosis
The good news is that the prognosis for many pediatric urological tumors, especially Wilms tumor when caught early, is excellent, with high survival rates. However, long-term follow-up is critical.
- Surveillance: Children require years of careful monitoring, including regular physical exams and imaging, to watch for recurrence or the development of new tumors.
- Monitoring Kidney Function: For those who have undergone nephrectomy, the single remaining kidney must be monitored for its entire life. The Pediatric Urologist in India works alongside the pediatric nephrologist to ensure the remaining kidney stays healthy.
- Fertility and Function: For testicular tumor survivors, monitoring for fertility issues and hormone deficiency is also an important part of the long-term care plan.
The specialization inherent in answering What is the difference between a pediatric urologist is underscored by this lifelong commitment to the child’s complex health needs.
Conclusion: Specialized Care for Complex Problems
Navigating a diagnosis of a pediatric urological tumor is challenging, but understanding What is the difference between a pediatric urologist and other specialists clarifies the path forward. You need a highly dedicated, specialized team to manage these rare cancers.
Specialists like Dr. Sujit Chowdhary are key members of this team, offering advanced surgical techniques, including minimally invasive and robotic approaches, for the safe and effective removal of tumors. His specific expertise as a Pediatric Urologist in India ensures that your child receives meticulous care focused on long-term functional and oncological outcomes.
Timely diagnosis and expert, specialized surgical care are the cornerstones of a successful recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. What are pediatric urological tumors?
Pediatric urological tumors are abnormal growths that occur in the kidneys, adrenal glands, bladder, or reproductive organs of children. They require highly specialized care from a Pediatric Urologist in India due to the delicate nature of a child’s developing urinary system.
Q2. What is the role of a pediatric urologist in tumor treatment?
A pediatric urologist manages the surgical treatment of urological tumors. They perform tumor removal (such as nephrectomy) and handle reconstructive procedures, ensuring preservation of kidney and urinary function whenever possible.
Q3. Do all kidney tumors in children require surgery immediately?
No. In many cases, especially with Wilms tumor, chemotherapy is given first to shrink the tumor. Surgery is performed after 4–6 weeks when it is safer and more effective.
Q4. Can testicular tumors in children be treated without removing the testicle?
Most malignant testicular tumors require removal of the affected testicle through an inguinal orchiectomy. This prevents spread and provides accurate diagnosis. The remaining testicle usually maintains normal hormone and fertility function.
Q5. Are pediatric urological tumors curable?
Many of these tumors—especially Wilms tumor—have high cure rates when detected early and treated by a multidisciplinary team. Long-term follow-up is essential to monitor kidney function and ensure no recurrence.